 android.support.v4.app.Fragment
android.support.v4.app.Fragment
|
||||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||
java.lang.Objectandroid.support.v4.app.Fragment
public class Fragment
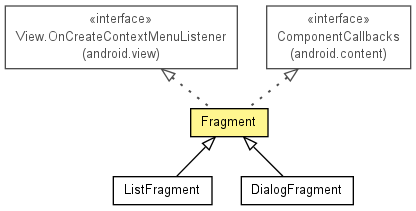
Static library support version of the framework's Fragment.
Used to write apps that run on platforms prior to Android 3.0. When running
on Android 3.0 or above, this implementation is still used; it does not try
to switch to the framework's implementation. See the framework SDK
documentation for a class overview.
| Nested Class Summary | |
|---|---|
static class |
Fragment.InstantiationException
Thrown by instantiate(Context, String, Bundle) when
there is an instantiation failure. |
static class |
Fragment.SavedState
State information that has been retrieved from a fragment instance through FragmentManager.saveFragmentInstanceState. |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
Fragment()
Default constructor. |
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
void |
dump(String prefix,
FileDescriptor fd,
PrintWriter writer,
String[] args)
Print the Fragments's state into the given stream. |
boolean |
equals(Object o)
Subclasses can not override equals(). |
FragmentActivity |
getActivity()
Return the Activity this fragment is currently associated with. |
android.os.Bundle |
getArguments()
Return the arguments supplied when the fragment was instantiated, if any. |
FragmentManager |
getChildFragmentManager()
Return a private FragmentManager for placing and managing Fragments inside of this Fragment. |
FragmentManager |
getFragmentManager()
Return the FragmentManager for interacting with fragments associated with this fragment's activity. |
int |
getId()
Return the identifier this fragment is known by. |
android.view.LayoutInflater |
getLayoutInflater(android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
|
LoaderManager |
getLoaderManager()
Return the LoaderManager for this fragment, creating it if needed. |
Fragment |
getParentFragment()
Returns the parent Fragment containing this Fragment. |
android.content.res.Resources |
getResources()
Return getActivity().getResources(). |
boolean |
getRetainInstance()
|
String |
getString(int resId)
Return a localized string from the application's package's default string table. |
String |
getString(int resId,
Object... formatArgs)
Return a localized formatted string from the application's package's default string table, substituting the format arguments as defined in Formatter and String.format(java.lang.String, java.lang.Object...). |
String |
getTag()
Get the tag name of the fragment, if specified. |
Fragment |
getTargetFragment()
Return the target fragment set by setTargetFragment(android.support.v4.app.Fragment, int). |
int |
getTargetRequestCode()
Return the target request code set by setTargetFragment(android.support.v4.app.Fragment, int). |
CharSequence |
getText(int resId)
Return a localized, styled CharSequence from the application's package's default string table. |
boolean |
getUserVisibleHint()
|
android.view.View |
getView()
Get the root view for the fragment's layout (the one returned by onCreateView(android.view.LayoutInflater, android.view.ViewGroup, android.os.Bundle)),
if provided. |
int |
hashCode()
Subclasses can not override hashCode(). |
static Fragment |
instantiate(android.content.Context context,
String fname)
Like instantiate(Context, String, Bundle) but with a null
argument Bundle. |
static Fragment |
instantiate(android.content.Context context,
String fname,
android.os.Bundle args)
Create a new instance of a Fragment with the given class name. |
boolean |
isAdded()
Return true if the fragment is currently added to its activity. |
boolean |
isDetached()
Return true if the fragment has been explicitly detached from the UI. |
boolean |
isHidden()
Return true if the fragment has been hidden. |
boolean |
isInLayout()
Return true if the layout is included as part of an activity view hierarchy via the <fragment> tag. |
boolean |
isRemoving()
Return true if this fragment is currently being removed from its activity. |
boolean |
isResumed()
Return true if the fragment is in the resumed state. |
boolean |
isVisible()
Return true if the fragment is currently visible to the user. |
void |
onActivityCreated(android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
Called when the fragment's activity has been created and this fragment's view hierarchy instantiated. |
void |
onActivityResult(int requestCode,
int resultCode,
android.content.Intent data)
Receive the result from a previous call to startActivityForResult(Intent, int). |
void |
onAttach(android.app.Activity activity)
Called when a fragment is first attached to its activity. |
void |
onConfigurationChanged(android.content.res.Configuration newConfig)
|
boolean |
onContextItemSelected(android.view.MenuItem item)
This hook is called whenever an item in a context menu is selected. |
void |
onCreate(android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
Called to do initial creation of a fragment. |
com.nineoldandroids.animation.Animator |
onCreateAnimator(int transit,
boolean enter,
int nextAnim)
Called when a fragment loads an animation. |
void |
onCreateContextMenu(android.view.ContextMenu menu,
android.view.View v,
android.view.ContextMenu.ContextMenuInfo menuInfo)
Called when a context menu for the view is about to be shown. |
void |
onCreateOptionsMenu(android.view.Menu menu,
android.view.MenuInflater inflater)
Initialize the contents of the Activity's standard options menu. |
android.view.View |
onCreateView(android.view.LayoutInflater inflater,
android.view.ViewGroup container,
android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
Called to have the fragment instantiate its user interface view. |
void |
onDestroy()
Called when the fragment is no longer in use. |
void |
onDestroyOptionsMenu()
Called when this fragment's option menu items are no longer being included in the overall options menu. |
void |
onDestroyView()
Called when the view previously created by onCreateView(android.view.LayoutInflater, android.view.ViewGroup, android.os.Bundle) has
been detached from the fragment. |
void |
onDetach()
Called when the fragment is no longer attached to its activity. |
void |
onHiddenChanged(boolean hidden)
Called when the hidden state (as returned by isHidden() of
the fragment has changed. |
void |
onInflate(android.app.Activity activity,
android.util.AttributeSet attrs,
android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
Called when a fragment is being created as part of a view layout inflation, typically from setting the content view of an activity. |
void |
onLowMemory()
|
boolean |
onOptionsItemSelected(android.view.MenuItem item)
This hook is called whenever an item in your options menu is selected. |
void |
onOptionsMenuClosed(android.view.Menu menu)
This hook is called whenever the options menu is being closed (either by the user canceling the menu with the back/menu button, or when an item is selected). |
void |
onPause()
Called when the Fragment is no longer resumed. |
void |
onPrepareOptionsMenu(android.view.Menu menu)
Prepare the Screen's standard options menu to be displayed. |
void |
onResume()
Called when the fragment is visible to the user and actively running. |
void |
onSaveInstanceState(android.os.Bundle outState)
Called to ask the fragment to save its current dynamic state, so it can later be reconstructed in a new instance of its process is restarted. |
void |
onStart()
Called when the Fragment is visible to the user. |
void |
onStop()
Called when the Fragment is no longer started. |
void |
onViewCreated(android.view.View view,
android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
Called immediately after onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup, Bundle)
has returned, but before any saved state has been restored in to the view. |
void |
onViewStateRestored(android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
Called when all saved state has been restored into the view hierarchy of the fragment. |
void |
registerForContextMenu(android.view.View view)
Registers a context menu to be shown for the given view (multiple views can show the context menu). |
void |
setArguments(android.os.Bundle args)
Supply the construction arguments for this fragment. |
void |
setHasOptionsMenu(boolean hasMenu)
Report that this fragment would like to participate in populating the options menu by receiving a call to onCreateOptionsMenu(android.view.Menu, android.view.MenuInflater)
and related methods. |
void |
setInitialSavedState(Fragment.SavedState state)
Set the initial saved state that this Fragment should restore itself from when first being constructed, as returned by FragmentManager.saveFragmentInstanceState. |
void |
setMenuVisibility(boolean menuVisible)
Set a hint for whether this fragment's menu should be visible. |
void |
setRetainInstance(boolean retain)
Control whether a fragment instance is retained across Activity re-creation (such as from a configuration change). |
void |
setTargetFragment(Fragment fragment,
int requestCode)
Optional target for this fragment. |
void |
setUserVisibleHint(boolean isVisibleToUser)
Set a hint to the system about whether this fragment's UI is currently visible to the user. |
void |
startActivity(android.content.Intent intent)
Call Activity.startActivity(Intent) on the fragment's
containing Activity. |
void |
startActivityForResult(android.content.Intent intent,
int requestCode)
Call Activity.startActivityForResult(Intent, int) on the fragment's
containing Activity. |
String |
toString()
|
void |
unregisterForContextMenu(android.view.View view)
Prevents a context menu to be shown for the given view. |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, finalize, getClass, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait |
| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public Fragment()
setArguments(android.os.Bundle)
and later retrieved by the Fragment with getArguments().
Applications should generally not implement a constructor. The
first place application code an run where the fragment is ready to
be used is in onAttach(Activity), the point where the fragment
is actually associated with its activity. Some applications may also
want to implement onInflate(android.app.Activity, android.util.AttributeSet, android.os.Bundle) to retrieve attributes from a
layout resource, though should take care here because this happens for
the fragment is attached to its activity.
| Method Detail |
|---|
public static Fragment instantiate(android.content.Context context,
String fname)
instantiate(Context, String, Bundle) but with a null
argument Bundle.
public static Fragment instantiate(android.content.Context context,
String fname,
android.os.Bundle args)
context - The calling context being used to instantiate the fragment.
This is currently just used to get its ClassLoader.fname - The class name of the fragment to instantiate.args - Bundle of arguments to supply to the fragment, which it
can retrieve with getArguments(). May be null.
InstantiationException - If there is a failure in instantiating
the given fragment class. This is a runtime exception; it is not
normally expected to happen.public final boolean equals(Object o)
equals in class Objectpublic final int hashCode()
hashCode in class Objectpublic String toString()
toString in class Objectpublic final int getId()
public final String getTag()
public void setArguments(android.os.Bundle args)
public final android.os.Bundle getArguments()
public void setInitialSavedState(Fragment.SavedState state)
FragmentManager.saveFragmentInstanceState.
state - The state the fragment should be restored from.
public void setTargetFragment(Fragment fragment,
int requestCode)
FragmentManager.putFragment().
fragment - The fragment that is the target of this one.requestCode - Optional request code, for convenience if you
are going to call back with onActivityResult(int, int, Intent).public final Fragment getTargetFragment()
setTargetFragment(android.support.v4.app.Fragment, int).
public final int getTargetRequestCode()
setTargetFragment(android.support.v4.app.Fragment, int).
public final FragmentActivity getActivity()
public final android.content.res.Resources getResources()
getActivity().getResources().
public final CharSequence getText(int resId)
resId - Resource id for the CharSequence textpublic final String getString(int resId)
resId - Resource id for the string
public final String getString(int resId,
Object... formatArgs)
Formatter and String.format(java.lang.String, java.lang.Object...).
resId - Resource id for the format stringformatArgs - The format arguments that will be used for substitution.public final FragmentManager getFragmentManager()
getActivity(), during the time from when the fragment is
placed in a FragmentTransaction until it is committed and
attached to its activity.
If this Fragment is a child of another Fragment, the FragmentManager
returned here will be the parent's getChildFragmentManager().
public final FragmentManager getChildFragmentManager()
public final Fragment getParentFragment()
public final boolean isAdded()
public final boolean isDetached()
FragmentTransaction.detach(Fragment) has been used on it.
public final boolean isRemoving()
public final boolean isInLayout()
public final boolean isResumed()
onResume() and onPause() as well.
public final boolean isVisible()
public final boolean isHidden()
onHiddenChanged(boolean). Note that the hidden state is orthogonal
to other states -- that is, to be visible to the user, a fragment
must be both started and not hidden.
public void onHiddenChanged(boolean hidden)
isHidden() of
the fragment has changed. Fragments start out not hidden; this will
be called whenever the fragment changes state from that.
hidden - True if the fragment is now hidden, false if it is not
visible.public void setRetainInstance(boolean retain)
onDestroy() will not be called (but onDetach() still
will be, because the fragment is being detached from its current activity).
onCreate(Bundle) will not be called since the fragment
is not being re-created.
onAttach(Activity) and onActivityCreated(Bundle) will
still be called.
public final boolean getRetainInstance()
public void setHasOptionsMenu(boolean hasMenu)
onCreateOptionsMenu(android.view.Menu, android.view.MenuInflater)
and related methods.
hasMenu - If true, the fragment has menu items to contribute.public void setMenuVisibility(boolean menuVisible)
menuVisible - The default is true, meaning the fragment's menu will
be shown as usual. If false, the user will not see the menu.public void setUserVisibleHint(boolean isVisibleToUser)
An app may set this to false to indicate that the fragment's UI is scrolled out of visibility or is otherwise not directly visible to the user. This may be used by the system to prioritize operations such as fragment lifecycle updates or loader ordering behavior.
isVisibleToUser - true if this fragment's UI is currently visible to the user (default),
false if it is not.public boolean getUserVisibleHint()
setUserVisibleHint(boolean)public LoaderManager getLoaderManager()
public void startActivity(android.content.Intent intent)
Activity.startActivity(Intent) on the fragment's
containing Activity.
public void startActivityForResult(android.content.Intent intent,
int requestCode)
Activity.startActivityForResult(Intent, int) on the fragment's
containing Activity.
public void onActivityResult(int requestCode,
int resultCode,
android.content.Intent data)
startActivityForResult(Intent, int). This follows the
related Activity API as described there in
Activity.onActivityResult(int, int, Intent).
requestCode - The integer request code originally supplied to
startActivityForResult(), allowing you to identify who this
result came from.resultCode - The integer result code returned by the child activity
through its setResult().data - An Intent, which can return result data to the caller
(various data can be attached to Intent "extras").public android.view.LayoutInflater getLayoutInflater(android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
public void onInflate(android.app.Activity activity,
android.util.AttributeSet attrs,
android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
onAttach(Activity) has been called; all you should do here is
parse the attributes and save them away.
This is called every time the fragment is inflated, even if it is being inflated into a new instance with saved state. It typically makes sense to re-parse the parameters each time, to allow them to change with different configurations.
Here is a typical implementation of a fragment that can take parameters
both through attributes supplied here as well from getArguments():
Note that parsing the XML attributes uses a "styleable" resource. The declaration for the styleable used here is:
The fragment can then be declared within its activity's content layout through a tag like this:
This fragment can also be created dynamically from arguments given at runtime in the arguments Bundle; here is an example of doing so at creation of the containing activity:
activity - The Activity that is inflating this fragment.attrs - The attributes at the tag where the fragment is
being created.savedInstanceState - If the fragment is being re-created from
a previous saved state, this is the state.public void onAttach(android.app.Activity activity)
onCreate(Bundle) will be called after this.
public com.nineoldandroids.animation.Animator onCreateAnimator(int transit,
boolean enter,
int nextAnim)
public void onCreate(android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
onAttach(Activity) and before
onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup, Bundle).
Note that this can be called while the fragment's activity is
still in the process of being created. As such, you can not rely
on things like the activity's content view hierarchy being initialized
at this point. If you want to do work once the activity itself is
created, see onActivityCreated(Bundle).
savedInstanceState - If the fragment is being re-created from
a previous saved state, this is the state.
public android.view.View onCreateView(android.view.LayoutInflater inflater,
android.view.ViewGroup container,
android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
onCreate(Bundle) and onActivityCreated(Bundle).
If you return a View from here, you will later be called in
onDestroyView() when the view is being released.
inflater - The LayoutInflater object that can be used to inflate
any views in the fragment,container - If non-null, this is the parent view that the fragment's
UI should be attached to. The fragment should not add the view itself,
but this can be used to generate the LayoutParams of the view.savedInstanceState - If non-null, this fragment is being re-constructed
from a previous saved state as given here.
public void onViewCreated(android.view.View view,
android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup, Bundle)
has returned, but before any saved state has been restored in to the view.
This gives subclasses a chance to initialize themselves once
they know their view hierarchy has been completely created. The fragment's
view hierarchy is not however attached to its parent at this point.
view - The View returned by onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup, Bundle).savedInstanceState - If non-null, this fragment is being re-constructed
from a previous saved state as given here.public android.view.View getView()
onCreateView(android.view.LayoutInflater, android.view.ViewGroup, android.os.Bundle)),
if provided.
public void onActivityCreated(android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
setRetainInstance(boolean) to retain their instance,
as this callback tells the fragment when it is fully associated with
the new activity instance. This is called after onCreateView(android.view.LayoutInflater, android.view.ViewGroup, android.os.Bundle)
and before onViewStateRestored(Bundle).
savedInstanceState - If the fragment is being re-created from
a previous saved state, this is the state.public void onViewStateRestored(android.os.Bundle savedInstanceState)
onActivityCreated(Bundle) and before
onStart().
savedInstanceState - If the fragment is being re-created from
a previous saved state, this is the state.public void onStart()
Activity.onStart of the containing
Activity's lifecycle.
public void onResume()
Activity.onResume of the containing
Activity's lifecycle.
public void onSaveInstanceState(android.os.Bundle outState)
onCreate(Bundle),
onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup, Bundle), and
onActivityCreated(Bundle).
This corresponds to Activity.onSaveInstanceState(Bundle) and most of the discussion there
applies here as well. Note however: this method may be called
at any time before onDestroy(). There are many situations
where a fragment may be mostly torn down (such as when placed on the
back stack with no UI showing), but its state will not be saved until
its owning activity actually needs to save its state.
outState - Bundle in which to place your saved state.public void onConfigurationChanged(android.content.res.Configuration newConfig)
onConfigurationChanged in interface android.content.ComponentCallbackspublic void onPause()
Activity.onPause of the containing
Activity's lifecycle.
public void onStop()
Activity.onStop of the containing
Activity's lifecycle.
public void onLowMemory()
onLowMemory in interface android.content.ComponentCallbackspublic void onDestroyView()
onCreateView(android.view.LayoutInflater, android.view.ViewGroup, android.os.Bundle) has
been detached from the fragment. The next time the fragment needs
to be displayed, a new view will be created. This is called
after onStop() and before onDestroy(). It is called
regardless of whether onCreateView(android.view.LayoutInflater, android.view.ViewGroup, android.os.Bundle) returned a
non-null view. Internally it is called after the view's state has
been saved but before it has been removed from its parent.
public void onDestroy()
onStop() and before onDetach().
public void onDetach()
onDestroy().
public void onCreateOptionsMenu(android.view.Menu menu,
android.view.MenuInflater inflater)
setHasOptionsMenu(boolean). See
Activity.onCreateOptionsMenu
for more information.
menu - The options menu in which you place your items.setHasOptionsMenu(boolean),
onPrepareOptionsMenu(android.view.Menu),
onOptionsItemSelected(android.view.MenuItem)public void onPrepareOptionsMenu(android.view.Menu menu)
Activity.onPrepareOptionsMenu
for more information.
menu - The options menu as last shown or first initialized by
onCreateOptionsMenu().setHasOptionsMenu(boolean),
onCreateOptionsMenu(android.view.Menu, android.view.MenuInflater)public void onDestroyOptionsMenu()
onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu, MenuInflater)
was not called).
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(android.view.MenuItem item)
Derived classes should call through to the base class for it to perform the default menu handling.
item - The menu item that was selected.
onCreateOptionsMenu(android.view.Menu, android.view.MenuInflater)public void onOptionsMenuClosed(android.view.Menu menu)
menu - The options menu as last shown or first initialized by
onCreateOptionsMenu().
public void onCreateContextMenu(android.view.ContextMenu menu,
android.view.View v,
android.view.ContextMenu.ContextMenuInfo menuInfo)
view is about to be shown.
Unlike onCreateOptionsMenu(android.view.Menu, android.view.MenuInflater), this will be called every
time the context menu is about to be shown and should be populated for
the view (or item inside the view for AdapterView subclasses,
this can be found in the menuInfo)).
Use onContextItemSelected(android.view.MenuItem) to know when an
item has been selected.
The default implementation calls up to
Activity.onCreateContextMenu, though
you can not call this implementation if you don't want that behavior.
It is not safe to hold onto the context menu after this method returns.
onCreateContextMenu in interface android.view.View.OnCreateContextMenuListenerpublic void registerForContextMenu(android.view.View view)
View.OnCreateContextMenuListener on the view to this fragment, so
#onCreateContextMenu(ContextMenu, View, ContextMenuInfo) will be
called when it is time to show the context menu.
view - The view that should show a context menu.unregisterForContextMenu(View)public void unregisterForContextMenu(android.view.View view)
View.OnCreateContextMenuListener on the view.
view - The view that should stop showing a context menu.registerForContextMenu(View)public boolean onContextItemSelected(android.view.MenuItem item)
Use MenuItem.getMenuInfo() to get extra information set by the
View that added this menu item.
Derived classes should call through to the base class for it to perform the default menu handling.
item - The context menu item that was selected.
public void dump(String prefix,
FileDescriptor fd,
PrintWriter writer,
String[] args)
prefix - Text to print at the front of each line.fd - The raw file descriptor that the dump is being sent to.writer - The PrintWriter to which you should dump your state. This will be
closed for you after you return.args - additional arguments to the dump request.
|
||||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||